Paediatric Hypertension: A Silent Health Risk in Children
By Priyambda Sahay
Reviewed by : Ujala Cygnus
February 13, 2026
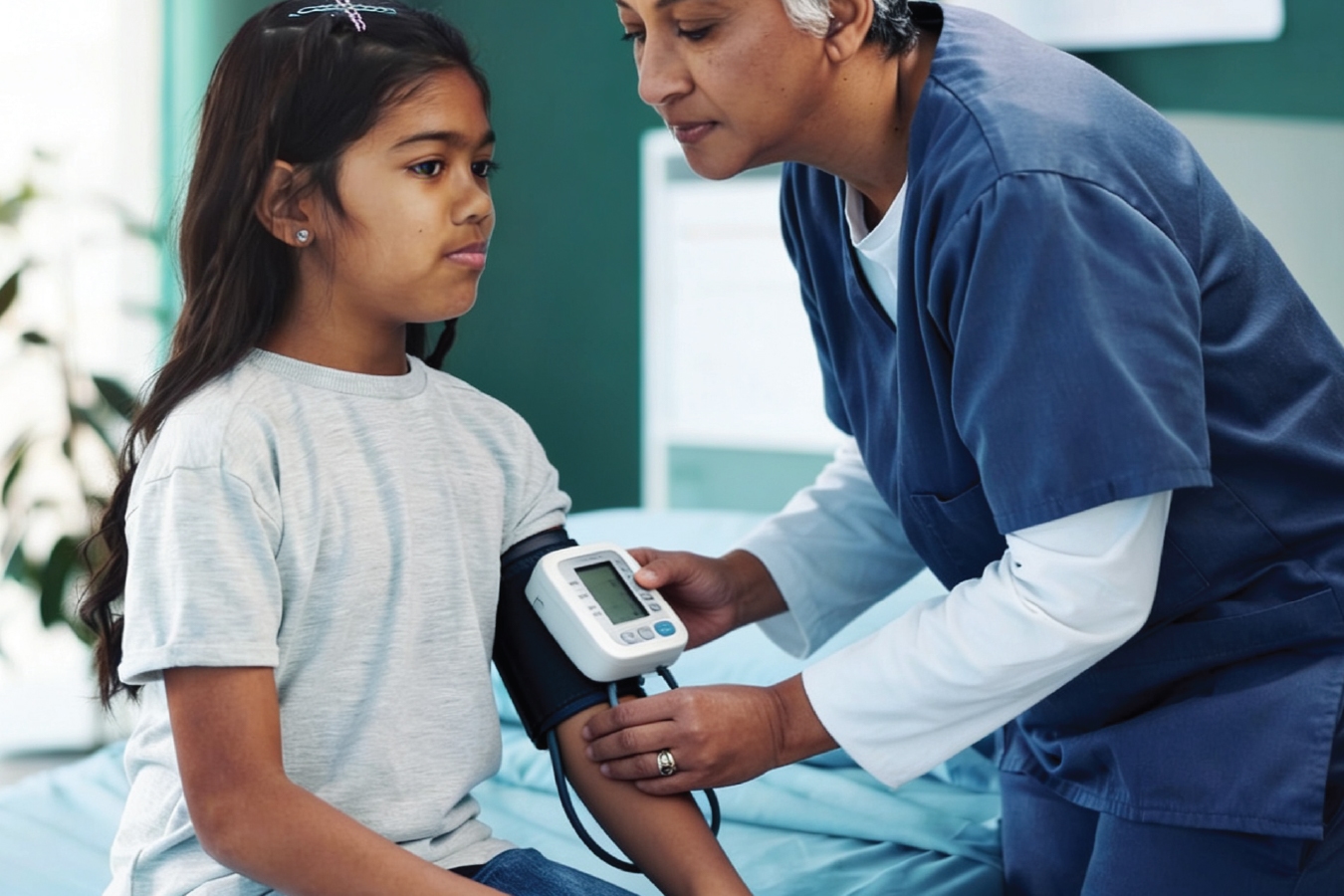
High blood pressure is often considered an adult health problem, but an increasing number of children and adolescents are now being diagnosed with paediatric hypertension. This emerging condition has become a significant public health concern due to changing lifestyles, rising childhood obesity, and lack of early screening.
Paediatric hypertension often goes unnoticed because it rarely causes obvious symptoms in its early stages. However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious long-term health complications, including heart disease, kidney problems, and stroke in adulthood.
Types of Paediatric Hypertension
Paediatric hypertension is broadly classified into two main types:
1. Primary Hypertension This type is more commonly seen in older children and adolescents. It is strongly associated with lifestyle-related factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy dietary habits, and a family history of hypertension.
2. Secondary Hypertension Secondary hypertension is more common in younger children and occurs because of an underlying medical condition. These may include kidney disease, congenital heart defects, hormonal disorders, or the use of certain medications.
In this context, Dr Akansha Arora, Paediatric Consultant at Ujala Cygnus Rainbow Hospital, Agra, has addressed several important questions related to paediatric hypertension, offering valuable insights for parents and caregivers.
How is paediatric hypertension different from adult hypertension?
Paediatric hypertension is defined based on age, gender, and height percentiles rather than fixed BP numbers, as in adults. In children, high blood pressure is often secondary to an underlying condition, whereas adult hypertension is usually primary. A child is diagnosed with hypertension when blood pressure readings are at or above the 95th percentile for their age, sex, and height on three separate occasions.
The readings are compared with standard pediatric blood pressure percentile curves. To identify any underlying cause, doctors may also recommend additional investigations such as blood and urine tests, ECG, echocardiography, and renal ultrasound.
Blood Pressure Categories in Children
Normal: Below the 90th percentile
Elevated: 90th–95th percentile
Hypertension: Above the 95th percentile
What are the common causes of high blood pressure in children?
Common causes include kidney diseases, congenital heart diseases, endocrine disorders, obesity or being overweight, sedentary lifestyle, high salt and junk food intake, lack of physical activity, excessive screen time, genetic factors, poor sleep pattern, stress, and certain medications such as steroids and stimulants.
What symptoms should parents watch for in children with hypertension?
In many cases, children with high blood pressure do not show symptoms. Hypertension in children is often asymptomatic, when symptoms do appear, they may include headache, dizziness, fatigue, vision problems, nosebleeds, poor growth or difficulty concentrating, severe hypertension may cause chest pain, shortness of breath or seizures. I would recommend regular blood pressure screening, especially for high-risk children, as symptoms are often absent in the early stages.
How can hypertension in children be prevented and managed?
Prevention and management focus on maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet with low salt intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and limiting screen time. Treating any underlying medical conditions is equally important. Medications may be prescribed if lifestyle changes are not effective, but only under strict medical supervision.
Can we use any BP measuring machine to check blood pressure in children?
No, measuring blood pressure in children requires paediatric-specific BP cuffs, a calm environment, and multiple readings taken across different visits. Unlike adults, children’s blood pressure is interpreted using age-, gender-, and height-based percentile charts, not a single fixed number. Using the correct cuff size is crucial, as adult cuffs or non-validated machines can lead to inaccurate or false readings.
Prevention Tips for Parents
Parents play a vital role in preventing paediatric hypertension. Encouraging children to engage in outdoor play and regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and heart health. Providing nutritious, home-cooked meals and limiting salty, packaged, and fast foods can significantly reduce risk factors. It is also important to monitor and limit screen time, ensure regular health check-ups, and have your child’s blood pressure checked during routine paediatric visits, especially if they are at higher risk.
Click here to book an appointment with Dr Akansha Arora .If you have specific questions about paediatric hypertension, please get in touch with the nearest Ujala Cygnus Hospital or reach our health experts at askadoctor@ujalacygnus.com.
FAQ
How Is Blood Pressure Measured in Children?
Blood pressure measurement in children requires Correct cuff size, Calm environment and Multiple readings. If a child is found to have high blood pressure, doctors may recommend Repeated BP measurements, Blood and urine tests, Kidney ultrasound, Echocardiography (heart evaluation) and Lifestyle assessment. These tests help determine whether hypertension is primary or secondary.
What are the treatments for Paediatric Hypertension?
The first line of treatment for paediatric hypertension is lifestyle modification. Most children respond well to healthy changes such as a balanced diet with reduced salt intake, regular physical activity, weight management, limited screen time, and adequate sleep. In some cases, medication may be required if blood pressure remains high despite lifestyle changes, if there is evidence of organ damage, or if the child has secondary hypertension. Treatment is always individualised, based on the child’s age, underlying cause, and overall health condition.
Why Early Detection Matters?
untreated, paediatric hypertension can lead to serious long-term complications such as heart enlargement, kidney damage, an increased risk of hypertension in adulthood, and early cardiovascular disease. Early diagnosis and timely intervention play a crucial role in preventing lifelong health issues and ensuring healthy growth and normal development in children.
Loading...