Lung Cancer- Causes, Types, Diagnosis & Treatments
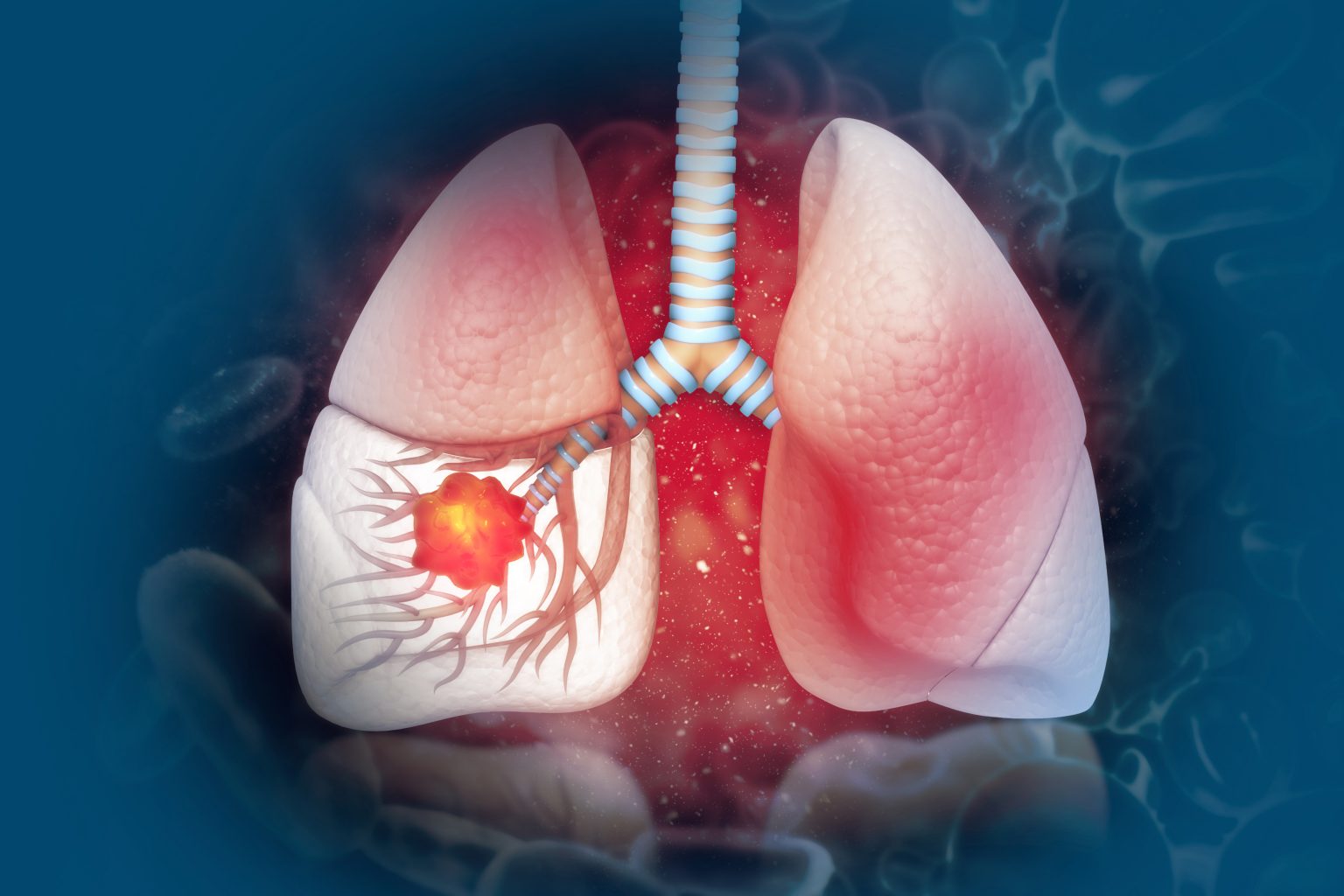
Lungs are two sponge-like air-sacs needed for breathing. When you breathe through your nose, air goes through a windpipe to your lungs in which oxygen is extracted and transported to other parts of the body, in the process, carbon dioxide is given out back through the windpipe.
When the cells in the lungs begin to grow out of control, it leads to lung cancer. Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally and becoming an epidemic in India.
Causes Of Lung Cancer
One of the biggest causes of lung cancer is smoking and breathing polluted and contaminated air. However, it is common for people who don’t smoke to also be affected by lung cancer. Generally, carcinogenic smoke damages the cells in the lungs making them cancerous and damage the lungs.
Early symptoms of the onset of lung cancer
- Regular cough, sometimes with small spouts of blood- Blocking of airways causes cough and inflammation of bleeding.
- Chest congestion and shortness of breath- With lung cancer, shortness of breath is a common symptom because of the accumulation of fluid in the lung that makes it hard to expand when inhaling.
- Headache, regular tiredness, and upper body weakness- When cancer spreads to the lining of the lungs and other body areas, there can be a pain in the chest, nausea, and headache.
Types Of Lung Cancer
Broadly, there are two types of lung cancer.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) – They include various other types of lung cancers such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. They are grouped in the same category because their treatment is similar. About 80-85% of people suffer from NSCLC.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) – They are more common in smokers. About 10-15% of lung cancers are SCLC. The cancerous cells metastasize quickly and grow quickly. The general treatment is chemotherapy and radiation therapy and occurs exclusively in heavy smokers.
- Carcinoid Tumors- They constitute about 5% of the lung cancers and tend to grow slowly.
Diagnosis Of Lung Cancer If you think that you suffer from lung cancer, consult a cancer specialist. The doctor may perform a number of tests including:
- Imaging tests- An X-Ray image of the chest may reveal, if any, abnormal growth of mass.
- CT- Scan- The doctor may advise for a CT scan to check for any small lesions in the lung that may not be visible in the X-ray.
- Biopsy- A sample of tissue is collected from the abnormal cells. This process is called a biopsy.
Treatment Of Lung Cancer If detected with lung cancer, a patient may undergo various treatments depending upon underlying health conditions and the stage of the factor or the choice of the patient.
- Radiation Therapy– High-powered energy beams are used to kill cancer cells. This is used for people who have locally advanced cancer.
- Chemotherapy– A number of drugs are used to kill the cancer cells. They are usually injected through veins. They are often used before performing surgery to remove the cancer cells from the lungs.
- Surgery– It is used to remove the cancerous cell from the lung. Surgery is preferred when cancer has not spread beyond the lung. A patient may be required to undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy along with surgery.
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy– It is also known as radiosurgery and is an intense radiation therapy where the radiations are aimed at the cancer cells from multiple angles. They are used for such cases in which surgery cannot be used to treat cancer.
- Targeted Drug Therapy– They are focused on treating specific abnormalities within cancer cells. Most of the times, they are used to treat those who suffer from advanced or recurrent cancer.
- Immunotherapy– The body’s very own immune system is used to fight against cancer. Immunotherapy works by interfering with the ability of cancer cells that produce proteins that help them to hide from the immune system cells.
